7 Agricultural Revolutions That Will Change the Way We Farm
- James Wilson
- 0 Comments
Revolutionary farming has brought a number of cultural transformations that are set to make our lives better. In the world we live in today, it’s only a must to learn the different ways farming is changing the world.
When our ancestors first learned how to farm, it revolutionized the way we live. Farming changed our nomadic, hunter-gathering lifestyle to that of now permanent farming settlers. With farming providing a constant supply of food — time spent gathering and searching for food was now freed for other tasks. We now had the time to develop mathematics, sciences, the arts, culture, and eventually human civilization as we know it. However, with changing conditions and rising demand for food, farmers today must adapt and rise to the challenge. And to do so, farmers are going to have to rely on more than just tractors and mills if they want to feed the world.
In this article, we’re going to take a look at five technologies that will usher in the 4th agricultural revolution. From smart farming to GMOs, we’re going to look at technologies that’ll change how we farm our food.
Vertical Farming
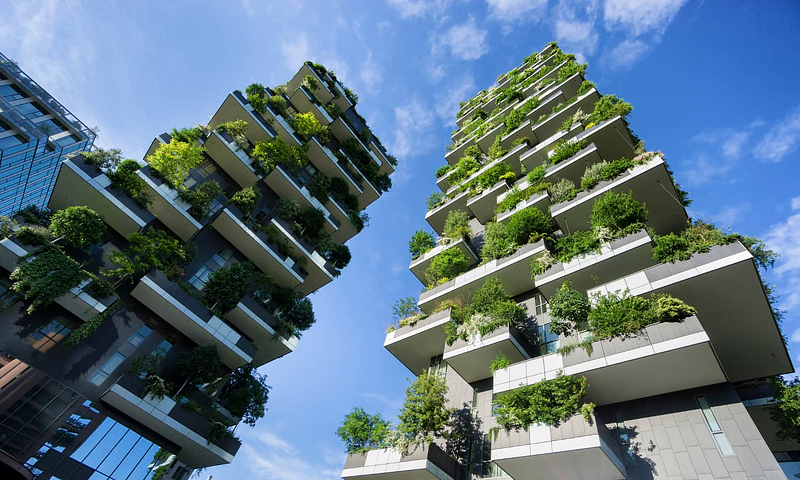

Every year, we lose an estimated 3 million hectares of farmland to urban development, erosion, and pollution and. With the booming population set to convert farmland into urban housing, farmers are faced with the problem of losing space for their crops.
To tackle this problem, architects and engineers have proposed that farmers change how they farm. Why look for wide swathes of land when farmers could take their crops upward through vertical farming? As the name implies, rather than using a wide piece of land, farmers are to scale their farms vertically — growing crops in a stacked manner. This can range anywhere from using leveled farms, with crops growing at various heights in warehouses to towering farming skyscrapers.
Vertical farming brings many advantages compared to traditional farming. As vertical farms can be accommodated in cities, fresh, delicious vegetables can now be available just a couple of blocks away! Furthermore, vertical farming permits farmers greater control over their crops. With all the crops compacted in a much smaller space, farmers can utilize atmospheric controls, special UV lights, and other ways to optimize crop growth.
Of course, researchers and agriculturists are still finding ways to resolve the economic issues of vertical farming. Starting a vertical farm requires a large amount of capital and has other overhead costs such as office occupancy, property tax, etc.
As the amount of viable farmland decreases every year, vertical farming is looking to be one of the better solutions for building new farms. If you’re looking for in-depth insights on vertical farming, you can go take a look at the book “The Vertical Farm: Feeding the World in the 21st Century”. The book gives you an in-depth analysis of the differences and advantages that vertical farms have over traditional farming.
Aeroponics and Hydroponics

To grow good crops, farmers must tend to the crop’s nutritional needs. Crops require minerals, water, and other nutrients — most of which are all carried by soil. The lack of fertile soil has become a major problem for farmers, with less and less fertile soil available each year. Factors such as pollution, erosion, and increasing urban development are the cause of fertile soil loss — tainting good soil and making it unusable. Due to dwindling fertile soil, farmers need to find creative ways to nourish their crops.
So how do agriculturists and researchers plan to fix the soil problem? It’s simple — by avoiding soil entirely and growing crops without soil. Hydroponics and aeroponics are technologies that allow farmers to grow crops without using soil. In the case of hydroponics, crops are grown in a nutrient-rich water solution. For aeroponics, plants can instead be grown in the air through the use of nutrient mists!
Economists expect the aeroponics and hydroponics industry to be valued together at an estimated USD 12 billion in 2025! This technology is expected to see more widespread use as farmers adapt and integrate the technology into their craft.
Farmers don’t have to be the only ones who benefit from aeroponics and hydroponics! Because of the reduced soil need, these technology systems can be compact and be made available for home use! Why not farm your own vegetables using the Vivosun Two-in-One Indoor hydroponic system! It’ll have everything you need to grow the vegetables for your next meal indoors!
Cultured Meat

We consume 315 million tons of meat annually, worldwide. The demand for meat is expected to increase further in the next several decades. Unfortunately, livestock farmers are struggling to find ways to scale up production. Raising and caring for livestock requires food, water, and plenty of lands — all of which are scarce and expensive.
To satisfy the demand for meat, rather than raise livestock, biologists have developed ways to grow meat in Petri dishes. This lab-grown meat is called cultured meat — which is produced by growing in vitro animal cells to create tissues. Cultured meat can be easily mass-produced in a matter of days, and will require less space, food, and water to grow!
Does this mean we’ll be able to grow wagyu steaks for dimes a dozen? Not yet. Different types of meat are the result of different muscle and fat tissue compositions. Currently, researchers aren’t able to control the meat “growing” process to a degree that can replicate good steak. Eventually, cultured meat might just replace “conventional meat”, and make us rethink and reconsider the ethics of meat production.
Meat, its consumption, and the ethics behind meat production is a surprisingly nuanced topic. Why do we consume meat even though meat is expensive and difficult to produce? Why have we produced a culture around meat despite the health hazards? If you’re interested in learning more, read “Meathooked: The History and Science of Our 2.5-Million-Year Obsession with Meat”. This book cuts through science, culture, and psychology to explore why we’re hooked on meat.
Smart Farms

Agriculture is not the most tech-savvy industry. Surely, farmers have tried their best to integrate technologies into their craft — from tractors to large wheat harvesters. However, computer scientists and industrial engineers have been developing ways to level up farms with technology.
Smart farms are just that — a means for farms to integrate data analytics and automation into the production scheme. Rather than farmers making predictions and forecasts themselves, farmers can utilize data analytics software to help them plan their next crop — using market data, demand, etc. Using tools like data analytics allows farms to rapidly adjust to the ever-changing demands of the market.
Smart farms will also come with state of the art sensors. These sensors will provide farmers key data on crop growth, pest control, moisture, etc. With the addition of drone automation — farmers will be able to control the crop growth process to extreme precision.
GMO Crops and Livestock

To create the modern cow we see today, it would take several decades of selective breeding. Breeding livestock for ideal traits such as hardiness or bigger produce is a difficult art — and doesn’t always succeed. With rapidly changing conditions due to climate change, pollution, and emerging livestock diseases, traditional breeding won’t provide hardier breeds fast enough for the market.
Fortunately for us, geneticists have found a way to circumvent breeding entirely. Through the use of gene editing, farmers can produce hardier livestock and crops in a matter of months instead of decades. Gene editing is precise, cost-effective, and more importantly much faster than traditional breeding methods. The more amazing thing about gene-editing however, is the ability to combine traits between two different organisms!
An example of this is BT Corn. BT Corn is called so because it’s been hybridized with the genes of Bacillus thuringiensis, a bacteria which produces a natural insecticide. As a result of gene editing, Bt corn can produce this insecticide as well, allowing it to be pest-resistant and hardier than normal corn. Fortunately for us, the insecticide the corn produces is safe for consumption!
Though there has been debate as to the safety of GM crops and livestock, GMO’s are likely going to be center-stage in the future of farming. The powers of gene-editing have much bigger potential than just GMO crops and livestock, however. And whether we’re prepared to use these powers with responsibility is another question.
Will we use gene-editing to create abominations? Create the perfect human and doom us to extinction? These questions are all explored through the wonderful book, “A Crack in Creation: Gene Editing and the Unthinkable Power to Control Evolution”.
Do you want to learn more about how technological advancement is changing the world for the better. Read these top 7 technologies that are set to change our lifestyle forever.